AutoCAD: The Essential Guide to Learn 25 Core CAD Concepts

AutoCAD is Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software used by various industries, such as architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing, to design floor plans, site plans, and mechanical assemblies. Its robust set of tools helps to draw objects accurately and precisely. Objects created in AutoCAD are meant to be replicated in real-world scenarios.
Now the question arises, with 1000s of features, how do you start learning AutoCAD? After years of experience, beginning to use AutoCAD in High School, I have developed 25 essential concepts of AutoCAD to master the top-notch design software. Once you master these concepts, you will have a solid foundational understanding of AutoCAD, which will help you succeed in your class and career.
AutoCAD User Interface
AutoCAD has a comprehensive user interface, and it’s essential to know each part of it; here’s why – Let’s say you want to fly a helicopter. Unless you know what and where the navigational tools or buttons are, you will not be able to understand how to fly it. The same goes with AutoCAD. Unless you know what each set of tools/buttons represents in AutoCAD, using AutoCAD will take a very long time. You don’t need to know where every single button is, but you need to know what and where the following sets of tools are located in the user interface:
- Application Menu
- File Tabs
- Quick Access Toolbar
- Ribbon Area
- Info Bar
- Command Window
- View Cube
- Selection Cursor
- Navigation Bar
- UCS
- Layout Tabs
- Command Line Palette
- Graphics Screen
- Workspace Switching Button
- Status Bar
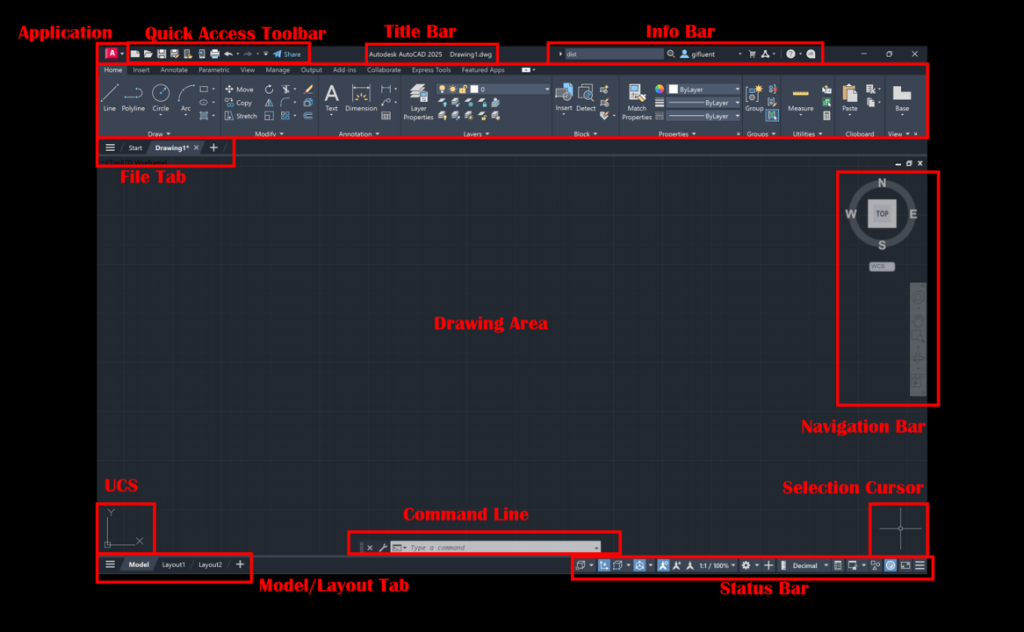
Do check out my blog A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering the AutoCAD User Interface to learn more about the AutoCAD user interface.
Navigational Tools in AutoCAD
To successfully navigate AutoCAD, you must know how to select, pan, and zoom using your mouse. Panning and zooming are straightforward. You can pan by holding the left side of your mouse and dragging different parts of the model space. You can zoom in and out by scrolling the mouse wheel up & down. However, there are multiple facets and nuances when it comes to selecting. You can select objects by clicking on them, you can do a selection window, you can make a lasso selection, you can choose similar objects, and a lot more. Check out my blog Effortlessly Learn AutoCAD Navigational Tools: Tips for Zoom, Pan, and Selection to learn more about the various AutoCAD navigational tools in depth.

AutoCAD Units and Limits
AutoCAD allows us to draw things to scale, and we need to make sure we are drawing using the correct units. In AutoCAD, you can use various units such as feet, meters, inches, centimeters, and millimeters. There are different options for displaying dimensions, such as architectural, engineering, decimal, fractional, and scientific formats. While an architect would choose to have the dimensions in architectural type, a civil engineer would generally prefer decimal type. There are also different ways to display angles, such as decimal degrees, degree/minute/second, grads, radians, and surveyor’s units.
You can set limits on the drawing area, which is helpful if you are drawing something on a 1:1 scale and want to seek the exact size of the end product. Setting a template with those configurations is not a bad idea if you use the same unit types and limits regularly. With templates, you can set not only units and limits but also various styles and configurations. Check out my blog 5 Essential Concepts to Master Units and Limits in AutoCAD to learn more about units and limits in AutoCAD.
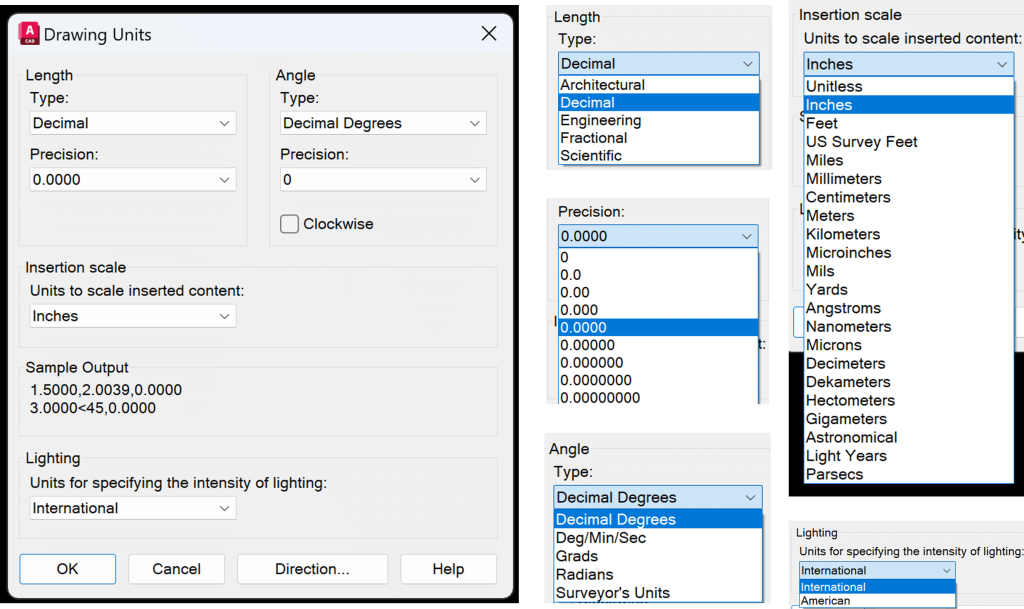
AutoCAD Model Space and Coordinate System
The model space is a limitless 3D drawing area where you can create drawing elements with appropriate units of your choice. AutoCAD has two essential coordinate systems: the World Coordinate System and the User Coordinate System. The WCS is a global reference and cannot be rotated, moved, or scaled. On the other hand, the UCS is movable and customizable based on the user. UCS offers a cartesian and polar coordinate system. Cartesian coordinates help work with linear elements, and polar coordinates help work with circular features. To learn more, checkout my blog on AutoCAD Coordinate System.

AutoCAD Drawing Tools – One Dimensional
There are a wide range of one-dimensional drawing tools available for drafting including line, polyline, arc, elliptical arc, spline, point, construction line, and ray. Each of these tools has its own specific function in AutoCAD which you can learn more in my blog post 8 Essential One-Dimensional Drawing Tools in AutoCAD.

AutoCAD Drawing Tools – Two Dimensional
You can draw multiple two-dimensional elements using AutoCAD such as Circle, Rectangle, Polygon, Ellipse, Revision Cloud, Region and Donut. To learn more about these two-dimensional elements, do check out my blog AutoCAD Drawing Tools – 6 Two Dimensional Drawing Tools to Master.
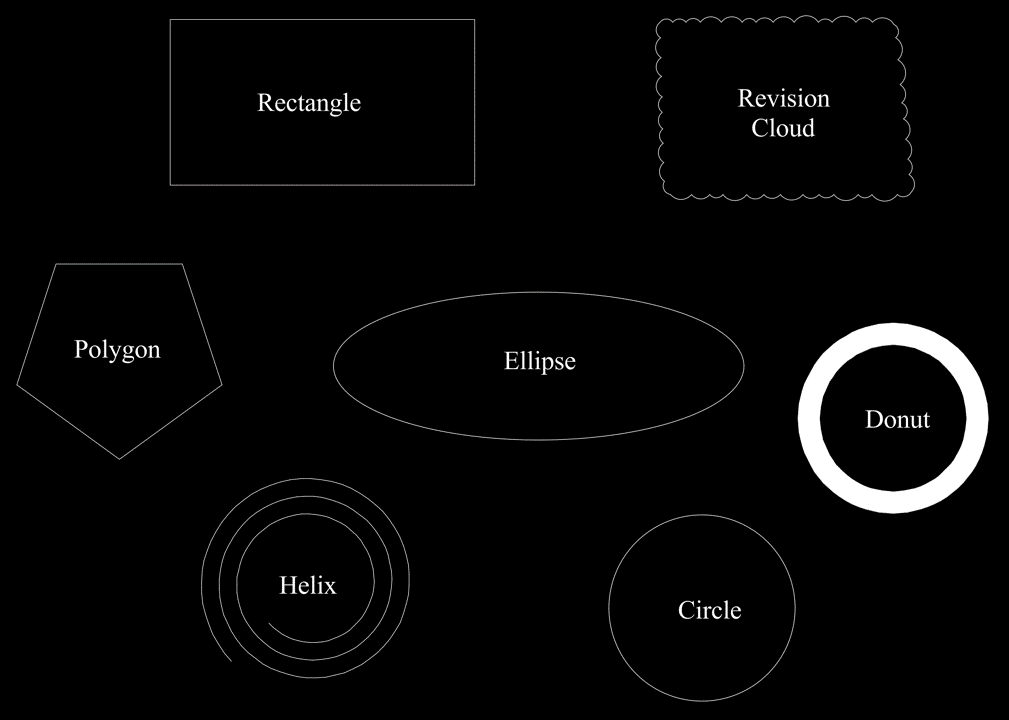
AutoCAD Object Snap, Ortho Mode and Polar Tracking
Object Snap, Ortho Mode, and Polar Tracking are essential skills for AutoCAD users seeking to produce accurate and precise drawings. The Snap Mode in AutoCAD allows you to specify exact points on lines or 2D objects by snapping the cursor to predefined points. Some of the commonly used snaps include endpoints, midpoints, and intersections. With Ortho mode, you can create straight lines by restricting cursor movement in horizontal and vertical directions. Polar tracking helps create lines at specific angles relative to a reference point or line. Check out my blog Mastering AutoCAD Object Snaps, Ortho Mode and Polar Tracking: 3 Key Tools for Precision.
Intuitive AutoCAD Tools and Commands
Below are a list of intuitive AutoCAD Tools and Commands. You can learn about them in more detail in my blog 11 Essential AutoCAD Intuitive Commands.
- New: Initiate the creation of a new drawing file.
- Template: A pre-designed file that contains specific settings and styles configuration.
- Open: Access an existing file to edit or in read-only mode.
- Save: Save changes made to the current drawing file
- Save As: Save the current drawing file under a new name or format.
- Cut: Remove selected objects from a drawing and place them on the clipboard, allowing you to paste them into an existing file or another file
- Copy: Duplicate an object to be placed in the current or another file.
- Paste: Insert objects from the clipboard.
- Undo: Reverse any edits made in the drawing.
- Redo: Reverse the effect of last undo while still in the undo command.
- Regen: Regenerates CAD interface
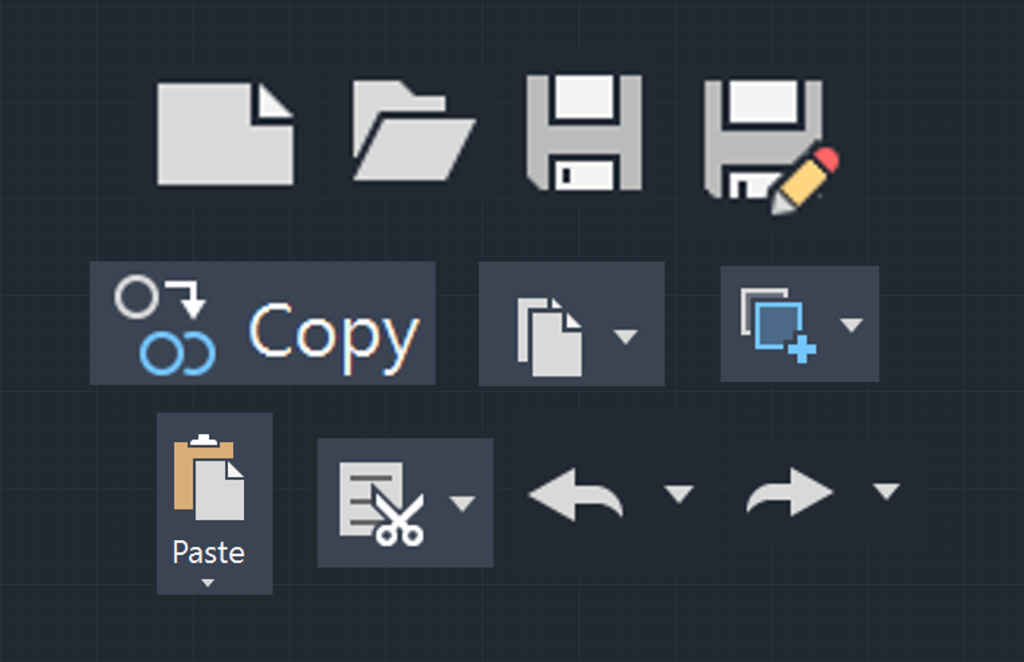
Basic AutoCAD Modify Tools
Below is a list of Basic Modify Tools in AutoCAD. Learn these tools in more detail in my blog 13 Basic Modify Commands in AutoCAD 2025.
- Move: Relocate object(s) from one location to another
- Rotate: Modifies the orientation of the object(s)
- Trim: Removes portions of objects that extend beyond the boundaries of other objects within the drawing
- Extend: Extends lines or objects to meet other objects.
- Mirror: Creates a mirrored copy of selected object(s) based on a specified line or axis
- Offset: Creates parallel copies of selected lines, polylines, or curves at a specified distance
- Scale: Resizes selected objects based on specified scale factor
- Fillet: Create a curved transition between two lines
- Chamfer: Bevels the corners of objects by removing a portion of the corner
- Join: Connects multiple lines, arcs, or polylines to form a single continuous object
- Explode: Breaks complex objects in individual components
- Stretch: Stretches objects between two specified points.
- Lengthen: Lengths selected object such as line, polyline, and arc.
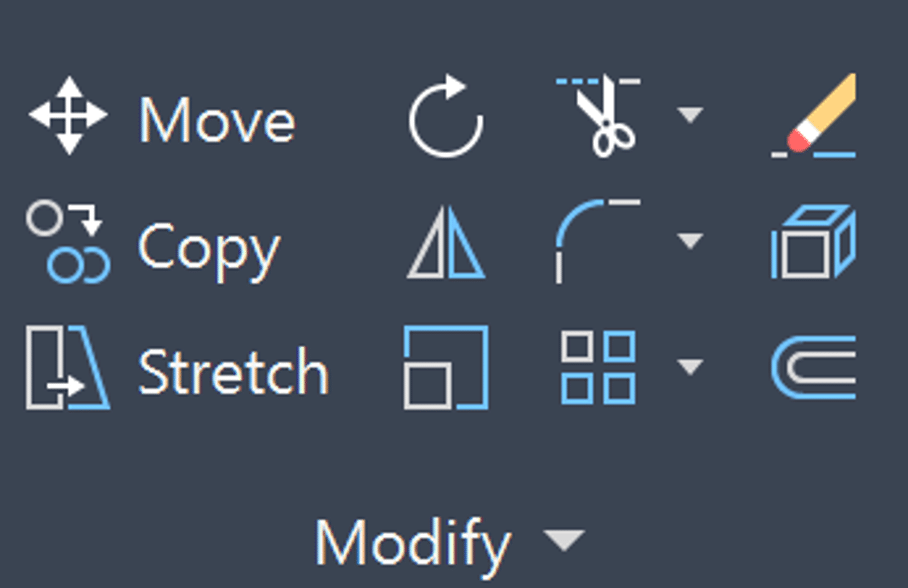
Advanced AutoCAD Modify Tools
Below are a list of Advanced Modify Tools in AutoCAD. Learn these tools in more detail in my blog 11 Advanced AutoCAD Modify Tools.
- Change Space: Move objects from paper space to model space and vice-versa
- NCopy: Copies selected items from an XREF. Also known as Nested Copy.
- Match Properties: Matches the properties of one object to another.
- Display Order: Determines the order in which objects and XREF are placed.
- Bpoly: Create a shrink-wrap around an existing boundary.
- Align: Move, rotate and scale (optional) objects in AutoCAD.
- Burst: Explode an object in AutoCAD by keeping text attributes.
- Pedit: Edit polylines in AutoCAD.
- Reverse: Switch the direction of a polyline.
- Blend: Connect two lines or curves using a spline.
- Mspace/Pspace: Change between model space and paper space.

AutoCAD Blocks, Dynamic Blocks and Count
AutoCAD has a feature called Blocks that eliminates the need to recreate commonly used objects. With this feature, you can reuse commonly used elements. Blocks are reusable objects in AutoCAD that can easily be inserted into your drawing to prevent you from repeatedly creating the same thing from scratch. For example, if you made a sofa in AutoCAD, you could easily reuse it by creating a block and inserting it in the drawing when needed.
The dynamic blocks take this feature to the next level, allowing users to manipulate a block with parameters. To keep an inventory or quantity take-off of these blocks and even other drawing elements, a feature called count tallies the occurrence of specific objects within a drawing. Learn more in my blog AutoCAD Block, Dynamic Block and Count for Efficient Design Creation.

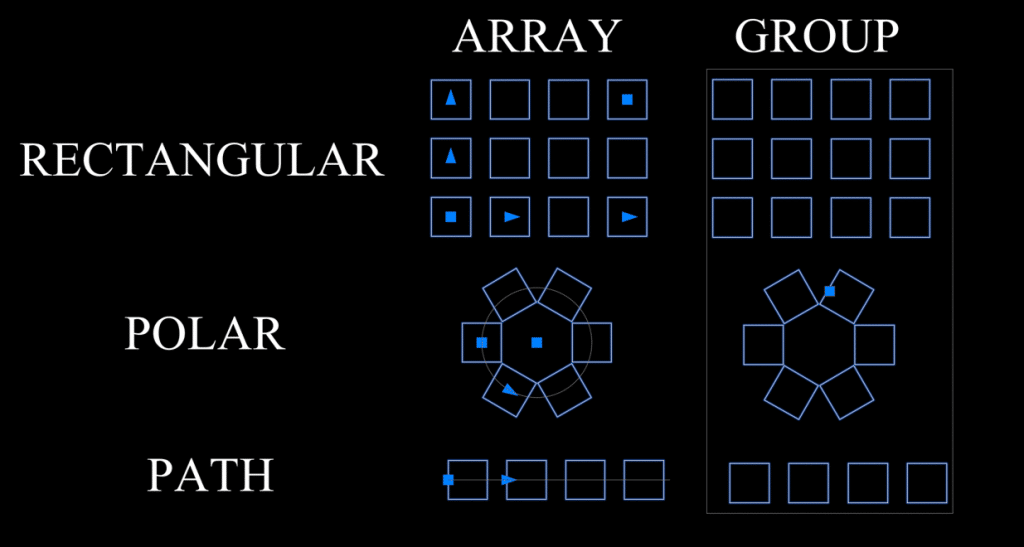
AutoCAD Array and Group
While arrays and groups are unrelated tools, they are great time-savers. Arrays help replicate objects in a controlled linear, rectangular, polar, and path-based pattern. This helps reduce your effort to put an object in a particular pattern manually. Groups provide a way to organize related objects into a single entity. Once you create a group, you can modify it in multiple ways, such as move, copy, rotate, and scale. Once you make your modifications, you can ungroup them, and the objects will return to their normal function. Check out my blog Effortlessly Learn AutoCAD Array and Group to learn more.
AutoCAD Layer
Learning the layer functionality is at the heart of AutoCAD. It enables users to control and organize AutoCAD’s visibility, properties, and object groupings. One can know what the object or linework represents based on the layer’s name. You can have the objects on the same layer be of the same color, same line type, same plot style, and much more. Layers can also be turned off and on, making it easy to display certain objects selectively. There are many nuances and tools related to layers in AutoCAD. I recommend checking out my blog post 38 Superb AutoCAD Layer Tools to learn more.

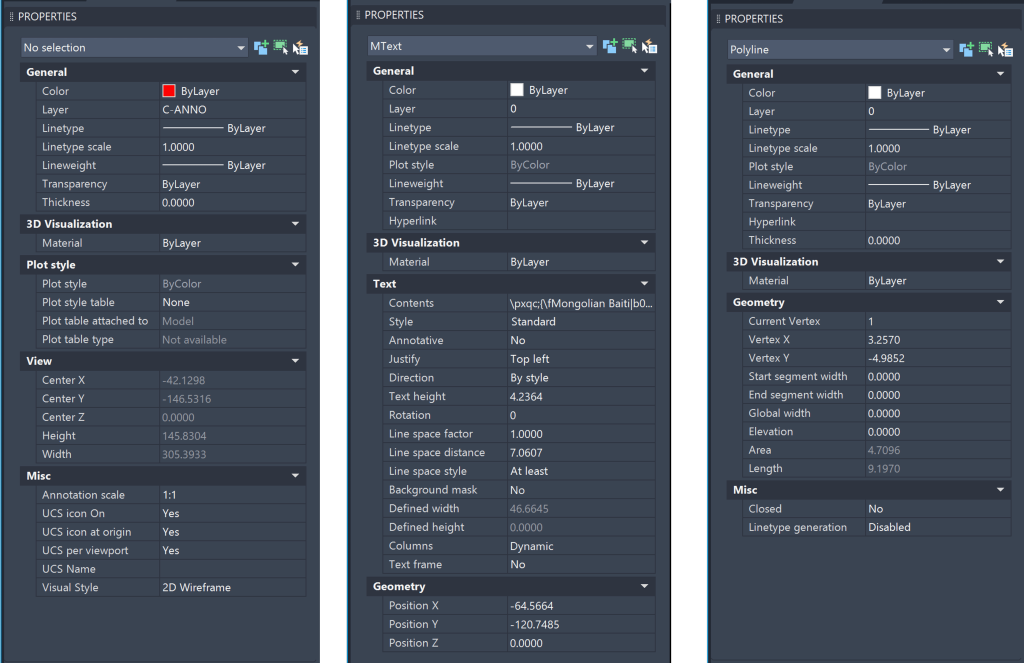
AutoCAD Properties Palette
Properties Panel is one of the fundamental features of AutoCAD that gives you quick access to the properties of selected objects within a drawing. Since the property panel centralizes modifying object properties, it eliminates the need to navigate multiple menus. Some editable parameters of a chosen object include layer, color, line type, dimension, and precision. Properties Panel is very user-friendly and helps enhance productivity.
AutoCAD Hatch and Gradient Fill
Hatches and gradients add visual and texture to AutoCAD drawings. Hatches represent a variety of materials, such as concrete and brick, in a closed area composed of patterns of lines, dots, or symbols. You can control a hatch’s scale, angle, color, and transparency. On the other hand, gradients are smooth transitions of colors or shading applied to an object. Checkout my blog Mastering 13 AutoCAD Hatch and Gradient Features: A Step-by-Step Guide for more information.

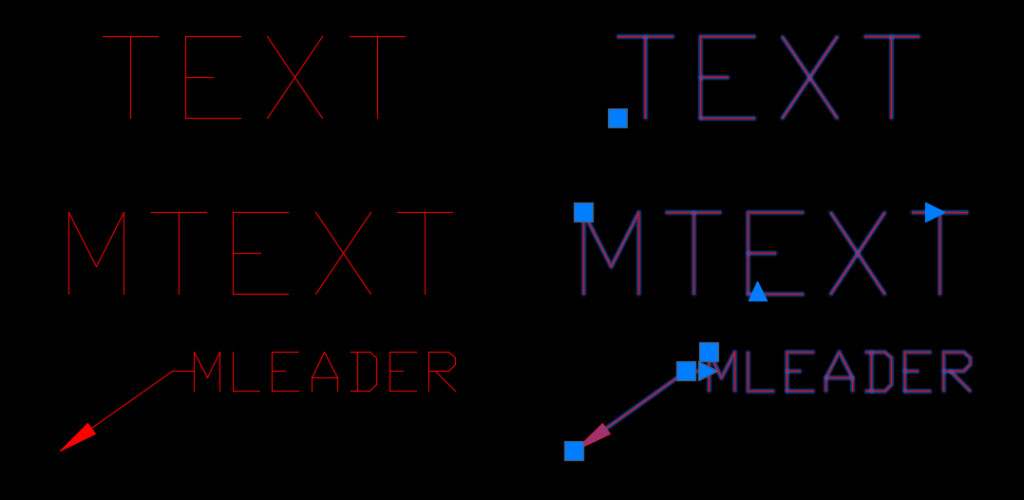
AutoCAD Text
AutoCAD has many text features similar to those in Microsoft Word or Google Doc, such as size, font, indent, bold, italicize, underline, etc. These features are intuitive and straightforward. There are three core AutoCAD-specific text features which are worth mastering – MText, MLeader and annotative scale. MText stands for multi-line text, facilitating easy editing and efficient formatting. MLeader allows you to add leader lines with text to drawings, enhancing the design’s clarity. Lastly, the annotation scale automatically enables text and dimension to adjust the size based on the viewport scale. Checkout my blog 9 AutoCAD Text and Annotation Pro Tips to learn more.
AutoCAD Dimension
Dimensions serve as critical elements in AutoCAD in accurately depicting the size and scale of objects in a given drawing. Linear dimensions, radial dimensions, angular dimensions, ordinate dimensions, and arc length dimensions are some of the commonly used dimensions in AutoCAD. You can also set up dimension styles to ensure dimensioning and drafting standards consistency. I explore these features in detail in my blog The Ultimate Guide to AutoCAD Dimensions.
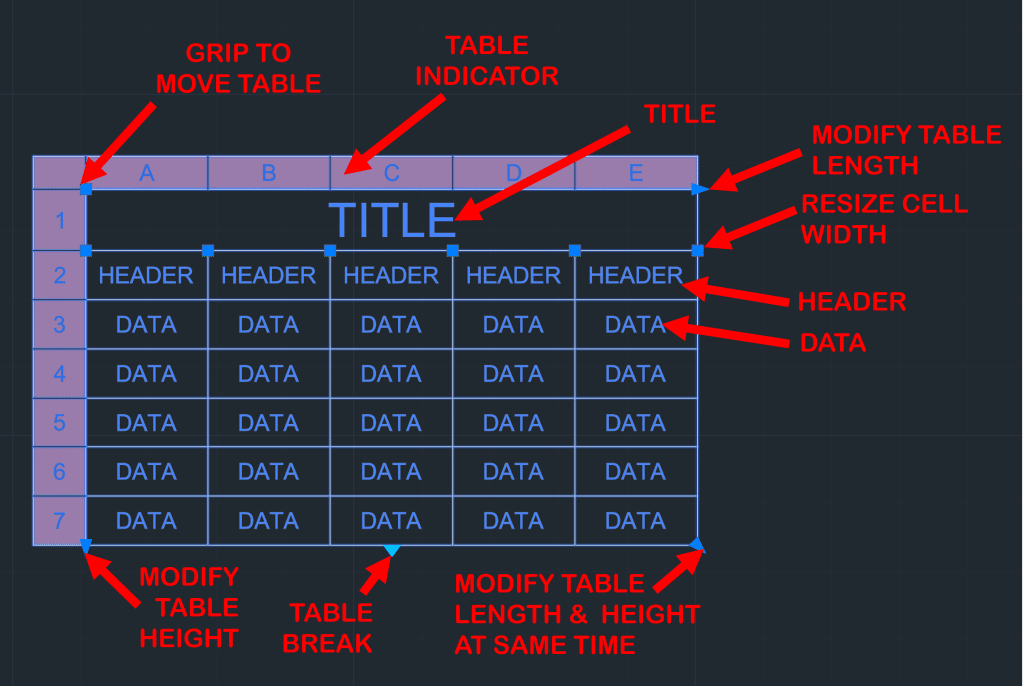
AutoCAD Table
Tables are helpful to organize and present tabular data within a drawing. You can create a table within AutoCAD, import a table from Excel, export a table to Excel, link a table to an Excel sheet, and much more. Checkout my blog AutoCAD Table Fundamentals: 5 Concepts to Boost Your Productivity to learn more.
AutoCAD External Reference
External Reference or XREF is a powerful tool in AutoCAD that helps users incorporate external drawings into current drawings, ensuring consistency, collaboration, and efficiency. XREF ensures consistency in that changes made to an XREF file will be reflected in all the drawings where it is referenced. XREF enables collaboration by dividing projects into multiple files and linking them together so that various users can work on different parts of the project simultaneously. XREF enhances efficiency by reducing file size since it references an external file rather than embedding it in the drawing. Apart from referencing XREFs, you can reference images, PDFs, and much more! Learn more about XREF in my blog AutoCAD XREF: The Secret Weapon of Efficient Design.

AutoCAD Paper Space or Layout
Layout space is a canvas for CAD designers to present their drawings at a specific scale on a standard-sized sheet. In the layout space, you can add title blocks, arrange multiple viewports, add scale, add notes, add north arrow, and other essential components to make your drawings professional. While model space helps design your project, paper space is beneficial in presenting your project efficiently. Checkout my blog 9 Key Things about AutoCAD Layout or Paper Space to learn more.
AutoCAD Print and Plot
Plotting in AutoCAD is the final step to bringing your digital design into physical plans. Various options for plot settings and customization are available, such as paper size, scale, orientation, plotting style, etc. Plot style is crucial to plotting since it controls the appearance of plotted objects, ensuring consistency in the final output. Another helpful aspect is the print preview, which can give you a quick preview of how your sheet will plot. Remember, all your efforts to build your AutoCAD project will be worthless unless you plot it. Learn more about AutoCAD Plot in my blog, Mastering AutoCAD Print: An Essential Guide to Professional Plotting.

AutoCAD File Maintenance – Purge, Audit, Overkill, Recover
Maintaining drawing efficiency and integrity is critical, and there are four significant tools to aid in this endeavor: Purge, Audit, Overkill, and Recovery. The Purge command allows you to remove unused objects in a CAD file, such as layers and line types, helping reduce file size. The Audit command fixes errors and corruption by detecting and repairing issues. The overkill command identifies and removes overlapping or duplicate objects. It sounds cool, but if you lose linework you were not anticipating, you can always undo it. Lastly, the recover command helps repair and recover corrupted files. These tools are helpful to safeguard your AutoCAD files against potential data loss and help enhance drawing quality. Learn more about these File Maintenance tools in my blog, Ultimate CAD File Maintenance using AutoCAD Purge, Audit, Overkill, and Recover Commands.

AutoCAD Sheet Set Manager
Sheet Set Manager in AutoCAD is all you need to organize your sheets, assign properties for each sheet, and plot them feasibly. In the sheet set manager, you can organize sheets chronologically and even add subsets to them. This optimizes collaboration as multiple team members can work on the same project individually by tackling different sheets. The best part about Sheet Set Manager is that you can assign sheet names, numbers, and other custom fields. You can add fields on each sheet and assign them to the sheet set manager. Hence, any time you change or rearrange sheet names or sheet numbers in the sheet set manager, it automatically updates on each sheet. You do not need to open and update each sheet. Lastly, the sheet set manager is a great tool for plotting or printing the whole set simultaneously, saving time and increasing efficiency. Learn more about Sheet Sets in my blog 13 FAQs on AutoCAD Sheet Set Manager.

AutoCAD Customization and Autolisp
Once you have a good grasp of AutoCAD, it will be a natural tendency to start customizing AutoCAD. You can customize the user interface, create custom line types, create custom hatches, create alias edits, create macros, and create custom commands using AutoLISP. Customization aims to streamline frequently used tools or processes and make AutoCAD more suited for your purpose.
AutoCAD System Variable
AutoCAD system variable lets you fine-tune how the software functions without having to manually adjust settings every time you work on a drawing.
My goal with this blog post is to give you a solid foundational understanding of AutoCAD. Mastering AutoCAD software will require more experience, working on projects, and time. Even AutoCAD experts who have used this software for years do not know every single feature or command. The goal here is not to learn everything but just enough to be comfortable with accomplishing tasks in CAD and continuously looking for ways to achieve the same tasks with fewer commands. I hope that once you go through these pillars of AutoCAD, you will be confident enough to navigate through AutoCAD, from starting a new drawing using a template to plotting the drawing to PDF.
I highly recommend using Autodesk documentation for AutoCAD, which gives detailed information on each command. I recommend nurturing your CAD skills by going through in-depth courses provided by Autodesk and watching videos on AutoCAD on Autodesk’s official website. Working in AutoCAD is a journey; there is much to learn, and Autodesk periodically adds new and valuable features. Good luck and best wishes as you venture on your AutoCAD journey!






